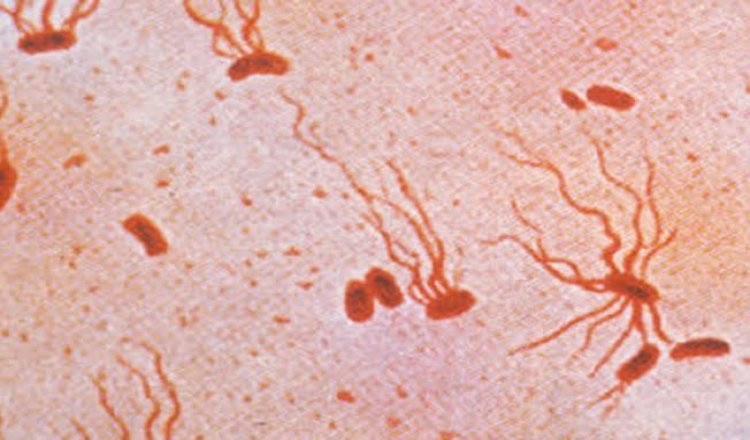
Pune doctors have recently identified two cases of typhoid that did not respond to ceftriaxone, the most common antibiotic used for treatment. Both patients, however, recovered after being given azithromycin, offering temporary relief but also raising concerns about growing resistance.
Health experts warn that while the number of such cases is still small, the situation can worsen quickly as bacteria are capable of spreading resistance to each other. Similar drug-resistant typhoid strains have already been reported in Gujarat and in neighbouring countries like Pakistan and Afghanistan, making it a matter of serious concern for India.
Doctors are calling for better monitoring and responsible use of antibiotics to prevent further resistance. They suggest that blood culture tests should be conducted before starting treatment so that accurate data on resistance patterns can be collected. Experts also highlight that overuse of antibiotics, both in humans and animals, is one of the key reasons behind this rising threat.

Rajasthan Faces Doctor Shortage Amid Recruitment Challenges
New Delhi: The Federation of Resident Doctors Association (FORDA) has urged the government to reconsider its guidelines regarding the minimum qualifications for critical care specialists.
FAIMA Launches Toll-Free Mental Health Helpline for Doctors Across India
Hyderabad Doctors Use Patient’s Appendix to Save His Kidneys
PHC Doctors’ Relay Hunger Strike Enters Seventh Day in Andhra Pradesh
We have various options to advertise with us including Events, Advertorials, Banners, Mailers, etc.